Hospital Architecture Design and Planning – Building the Future of Healthcare
Introduction
Hospitals serve as the lifeline of any community, offering spaces where lives are saved and wellness is restored. But have you ever considered how much thought goes into the architecture of these complex structures? Hospital architecture design and planning plays a pivotal role in creating an environment that is not only efficient and functional but also welcoming, healing, and sustainable. A well-designed hospital ensures that medical staff can work seamlessly while patients experience the utmost comfort and care. This delicate balance between function, aesthetics, and compliance makes hospital planning an intricate yet fascinating field of design.
From ancient healing temples to state-of-the-art medical facilities, the evolution of hospital design reflects advancements in healthcare, technology, and cultural priorities. Today, more than ever, thoughtful planning is required to address patient needs, staff efficiency, and environmental sustainability.
Understanding the Basics
Core Principles of Hospital Architecture
Hospital design revolves around three foundational principles: efficiency, safety, and patient-centric care. Designers must optimize spaces for medical workflows, prioritize infection control, and provide a comforting atmosphere for patients.
History and Evolution of Hospital Design
Early hospitals were rudimentary spaces designed primarily for care and quarantine. Over centuries, hospital design evolved, incorporating innovations like ventilation systems, natural lighting, and ergonomic layouts to support better healing environments. Modern hospitals, with their sleek designs and cutting-edge technologies, are a far cry from their predecessors.
Key Elements of Modern Hospital Planning
Modern hospital planning integrates technological advancements, sustainability, and inclusivity. This includes modular layouts, digital connectivity, and spaces designed to adapt to future healthcare demands.
Patient-Centered Design
Designing for Patient Comfort and Healing
A patient’s environment significantly impacts their recovery. Natural light, calming colors, private rooms, and access to green spaces are some of the features that enhance healing.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Hospital Layouts
Hospitals must be accessible to individuals of all abilities. This includes designing ramps, elevators, and signage for the visually impaired, as well as ensuring that all spaces are wheelchair-friendly.
Sustainability in Hospitals
Green Building Practices in Hospital Architecture
Sustainable hospital design prioritizes energy efficiency, reduced carbon footprints, and the use of eco-friendly materials. LEED-certified hospital buildings are becoming the gold standard globally.
Energy-Efficient Systems for Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals are energy-intensive, but incorporating solar panels, advanced HVAC systems, and LED lighting can significantly reduce energy consumption.
Water Management and Waste Reduction Strategies
Water-saving technologies, such as low-flow fixtures and rainwater harvesting systems, are vital for sustainable hospital operations. Proper waste segregation and recycling also play a crucial role.
Optimizing Functionality
Layouts for Operational Efficiency
A well-thought-out layout minimizes travel time for medical staff and patients while ensuring easy access to critical areas like operating rooms, ICUs, and labs.
Zoning and Space Allocation
Zoning divides hospitals into distinct areas based on their functions. This ensures a seamless flow of activities and reduces cross-contamination risks.
Effective Workflows in Hospital Planning
Hospital workflows should be mapped out during the design phase. For instance, locating emergency services near entrances ensures quicker patient triage and treatment.
Safety and Compliance
Meeting Health and Safety Standards
Hospitals must comply with stringent health and safety regulations to protect patients and staff. This includes infection control measures like HEPA filtration systems and antimicrobial surfaces.
Fire Safety and Emergency Preparedness
Fire escapes, sprinklers, and evacuation routes must be carefully planned to ensure the safety of everyone during emergencies.
Adhering to Building Codes and Medical Regulations
Architects must stay updated with local building codes and medical facility regulations, ensuring designs meet the required standards.
Technology Integration
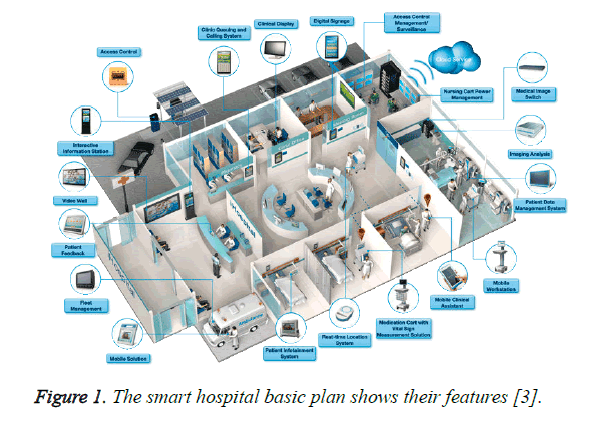
Smart Hospital Technologies and IoT
From automated patient check-ins to AI-powered diagnostics, technology is transforming hospitals. Architects now design spaces to accommodate smart technologies and IoT systems.
Designing for Future Healthcare Innovations
Hospitals should be built with adaptability in mind, allowing spaces to integrate future medical technologies, such as robotic-assisted surgeries or virtual consultations.
IT Infrastructure and Digital Connectivity
Hospitals require robust IT networks to support electronic health records, telemedicine, and other digital services.
Specialized Areas
Designing ICUs, Surgical Suites, and Patient Rooms
Specialized units demand meticulous design. For instance, ICUs require noise control and specialized ventilation, while surgical suites need sterile environments with advanced lighting.
Emergency Department Design
The emergency department must be designed for rapid response and patient triage, with easy access to diagnostic and surgical units.
Spaces for Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
Medical imaging areas must consider shielding requirements for radiation safety, alongside ergonomic designs for patient comfort.
Staff and Visitor Needs
Comfortable Spaces for Healthcare Staff
Break rooms, lounges, and on-site facilities like childcare centers are essential for staff well-being and productivity.
Visitor-Friendly Designs
Comfortable waiting areas, clear signage, and access to amenities like cafes and restrooms enhance the visitor experience.
Financial Planning
Cost-Efficient Hospital Design Strategies
Maximizing resource efficiency and choosing durable, low-maintenance materials helps reduce construction and operational costs.
Budgeting for Long-Term Maintenance
Effective maintenance planning ensures that hospitals remain functional and safe for decades.
Cultural and Regional Considerations
Incorporating Local Culture into Hospital Architecture
Reflecting local culture in hospital design fosters a sense of familiarity and community. This might include architectural styles or art inspired by local traditions.
Adapting to Environmental and Climatic Factors
Hospitals must be designed to withstand local climatic conditions, such as incorporating hurricane-resistant structures in coastal areas.
The Future of Hospital Design
Trends Shaping the Future of Healthcare Facilities
Innovations like modular construction, AI-driven design tools, and wellness-focused layouts are shaping the future of hospitals.
The Role of AI and Robotics in Hospital Architecture
AI and robotics are revolutionizing hospital planning, from optimizing space utilization to integrating automated systems for patient care.
Conclusion
Thoughtful hospital architecture design and planning go beyond bricks and mortar. It is about creating environments where patients heal faster, staff perform efficiently, and communities thrive. By combining innovation with sustainability and patient-centered care, we can shape the future of healthcare facilities to be truly inspiring and functional.
FAQs
How does hospital design impact patient recovery?
What are the core principles of hospital architecture design?
Why is sustainability important in hospital planning?
How do hospitals accommodate future technological advancements?
What role do cultural factors play in hospital architecture?
How can hospital designs improve staff efficiency and morale?
Inbound Link Suggestions:
- “Healthcare Innovations”
- “Sustainable Building Practices”
Outbound Link Suggestions: